Table of Contents
How Often Should You Eat Beef Heart
Beef heart is a nutrient-rich, affordable cut packed with protein, iron, zinc, and B12—great for muscle repair, energy, and oxygen circulation. To avoid excess nutrients, it’s best enjoyed 1–2 times per week. Pair with veggies, grains, and other proteins for a balanced meal.
Nutritional Benefits of How Often Should You Eat Beef Heart
Beef heart is a nutrient-dense organ meat, but how often should you eat beef heart to maximize its benefits? Rich in essential nutrients such as protein, iron, zinc, and B vitamins, including B12, beef heart supports energy production and red blood cell formation. It also contains coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), a powerful antioxidant that promotes heart health and cellular energy. Understanding how often you should eat beef heart ensures you get these nutrients without overconsumption. Including beef heart in your meals regularly can boost your nutrient intake, but moderation is key. Experts generally recommend consuming it 1–2 times per week. So, how often should you eat beef heart? Stick to these guidelines to enjoy its benefits safely and effectively.
High Protein Content: How Often Should You Eat Beef Heart
Beef heart is a lean, high-quality protein packed with all essential amino acids, making it great for muscle growth, repair, and overall health. It supports enzyme production, hormone balance, and immune function, while keeping you full and energized. Lower in fat than many beef cuts, it’s a smart choice for a protein-rich, balanced diet.
Rich in Essential Vitamins and Minerals: How Often Should You Eat Beef Heart
Beef heart is loaded with essential vitamins and minerals. It is particularly high in B vitamins, including B12, which helps maintain energy levels and supports nerve function. Additionally, beef heart is a rich source of iron, necessary for producing red blood cells, and zinc, which aids in immune system support. These nutrients make beef heart a powerhouse for nutrition.
Comparing Beef Heart to Other Meats
Beef Heart vs. Chicken Heart
When comparing beef heart to chicken heart, both are incredibly nutrient-dense and offer unique health benefits. Beef heart typically has a higher protein content and contains more CoQ10, an antioxidant that supports heart health and cellular energy. It also provides more iron, which helps maintain healthy blood levels and boosts overall energy.
On the other hand, chicken heart is smaller in size, lower in calories, and has a milder flavor, making it a great option for lighter meals or quick dishes. Chicken heart cooks faster and is often used in stir-fries, skewers, or soups.
While beef heart is richer in some nutrients, chicken heart is slightly easier to digest and has a softer texture. Both are excellent sources of protein and vitamins, so including them in your diet on a rotating basis can provide variety and balanced nutrition. Whether you choose beef heart or chicken heart depends on your taste preference, meal plans, and dietary goals.
Beef Heart vs. Beef Liver
Beef liver is another organ meat with impressive nutritional value, but it differs from beef heart in several ways. While beef heart is higher in protein and CoQ10, beef liver contains more vitamin A and copper. Both are excellent sources of iron and B vitamins, but liver’s higher vitamin A content requires more moderation to avoid overconsumption.
Health Benefits of Regular Consumption
Improved Cardiovascular Health
Eating beef heart regularly can benefit your heart health. It is rich in coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10), a nutrient that supports heart function by improving energy production in cells and reducing oxidative stress. CoQ10 can help maintain healthy blood pressure levels and lower the risk of heart disease when combined with a balanced diet and active lifestyle.
Boosted Energy Levels: How Often Should You Eat Beef Heart
Beef heart contains a high concentration of B vitamins, particularly vitamin B12. This vitamin is essential for converting food into energy and supporting red blood cell production. Regularly including beef heart in your meals can help fight fatigue and keep your energy levels high throughout the day.
Enhanced Muscle Growth and Repair
With its high protein content, beef heart is ideal for promoting muscle growth and recovery. Protein is essential for repairing muscle tissue, especially after exercise. Including beef heart in your diet provides a cost-effective way to meet your daily protein needs and maintain strong, healthy muscles.
Recommended Frequency of Consumption
General Guidelines for a Balanced Diet
When incorporating beef heart into your diet, balance is key. While it is nutrient-dense and offers many health benefits, moderation is important to ensure variety in your diet and prevent overconsumption of certain nutrients, like cholesterol or iron. A diverse diet ensures you get all the essential nutrients your body needs.
Weekly Consumption Recommendations
Health experts suggest eating beef heart about 1–2 times per week to enjoy its nutritional benefits—like protein, iron, and B vitamins—without overdoing nutrients like iron or cholesterol. Pair it with other proteins, veggies, and whole grains for a balanced diet. Rotating with other organ meats like liver or kidney adds variety and keeps meals interesting.
Factors Influencing Frequency
The frequency of consuming beef heart can vary based on your individual dietary needs, lifestyle, and health goals. For example:
- Athletes or active individuals may benefit from slightly more frequent consumption due to its high protein and nutrient content.
- Individuals with specific medical conditions, like high cholesterol, may need to limit intake and consult with a healthcare professional.
- Personal taste preferences and access to quality beef heart can also influence how often you include it in your diet.
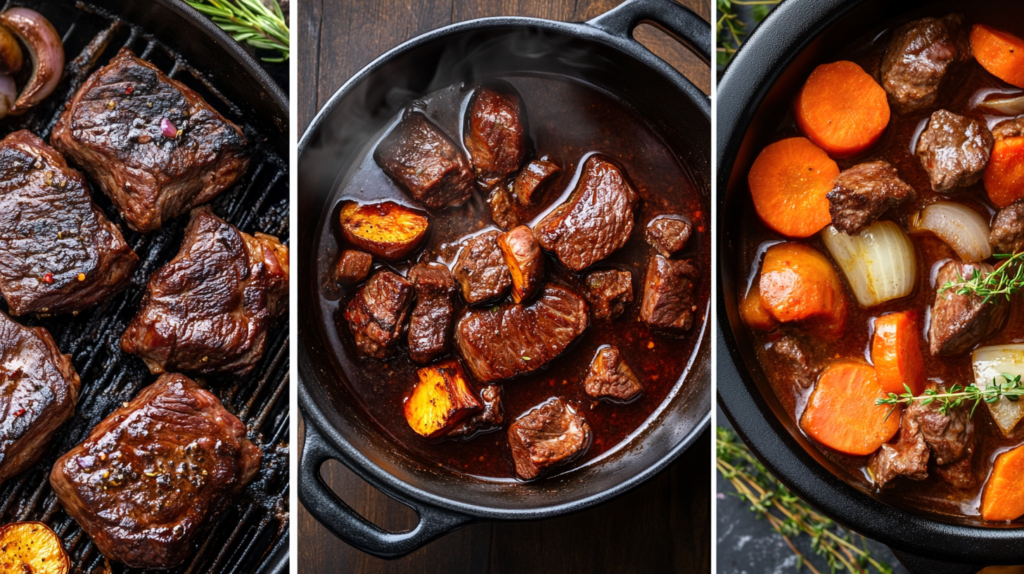

Preparing and Cooking Beef Heart
Tips for Selecting Quality Beef Heart
When buying beef heart, choose fresh, high-quality cuts from trusted sources. Look for the following:
- Freshness: The heart should be firm, moist, and have a bright red color.
- Source: Opt for grass-fed or organic beef heart, as these options often have better nutritional profiles and fewer additives.
- Trimmed or Whole: Decide whether to buy a whole heart or pre-trimmed portions, depending on your cooking plans.
Preparing beef heart correctly enhances its flavor and texture while preserving its nutritional benefits. With careful selection and preparation, you can create delicious, healthy meals.
Best Cooking Methods
Cooking beef heart properly is key to making it both delicious and nutritious. This cut of meat is lean, flavorful, and versatile, making it suitable for a variety of cooking techniques. Proper preparation helps maintain its texture, tenderness, and rich nutrient content. Below are some of the best cooking methods to try for a satisfying and healthy meal:
Grilling
Grilling beef heart brings out its natural flavors and adds a smoky touch. To prepare:
- Slice the heart into thin, even pieces for even cooking.
- Marinate with olive oil, garlic, and herbs to enhance flavor and tenderness.
- Grill over medium-high heat for about 2–3 minutes per side to achieve a tender and juicy texture.
Grilling is quick and maintains the heart’s nutrients while adding a slight char for extra flavor.
Braising
Braising is ideal for making beef heart tender and flavorful:
- Cut the heart into chunks and season with your favorite spices.
- Sear the pieces in a hot pan to lock in juices.
- Simmer in a flavorful liquid, such as broth or wine, for 2–3 hours until the meat is tender.
This method is perfect for creating hearty, comforting dishes.
Slow Cooking
Slow cooking allows beef heart to become incredibly tender and absorb flavors over time:
- Place the heart in a slow cooker with vegetables, herbs, and stock.
- Cook on low heat for 6–8 hours or high heat for 3–4 hours.
- Shred or slice before serving with a side of your choice.
convenient and makes the meat melt-in-your-mouth soft, perfect for stews or tacos.
Potential Risks and Precautions
Allergies and Sensitivities
Although rare, some individuals may experience allergies or sensitivities to beef heart. Symptoms can include digestive discomfort, skin reactions, or difficulty breathing. If you’re trying beef heart for the first time, start with a small portion to monitor your body’s response. If you have known allergies to beef or other organ meats, consult a healthcare provider before adding it to your diet.
Moderation is Key
While beef heart is packed with essential nutrients, it’s important to eat it in moderation. Overeating organ meats, including beef heart, can lead to excessive intake of certain nutrients like iron, cholesterol, or vitamin A, which may cause health issues over time. Too much iron can strain your liver, and high cholesterol levels might increase heart disease risks. To stay safe, experts recommend enjoying beef heart 1–2 times per week as part of a balanced diet. Pair it with vegetables and whole grains to create well-rounded, nutrient-rich meals.
To avoid potential risks:
- Limit consumption to 1–2 servings per week.
- Pair beef heart with a balanced diet that includes vegetables, whole grains, and other protein sources.
- If you have specific dietary restrictions or health conditions, seek guidance from a dietitian or healthcare professional.
By taking these precautions, you can enjoy the benefits of beef heart without compromising your health.
Frequently Asked Questions: How Often Should You Eat Beef Heart
Is beef heart good for weight loss?
Yes, beef heart is high in protein and low in fat, making it a filling and nutrient-dense option for weight loss. Learn more about healthy protein choices.
Can you eat beef heart every day?
It is better to eat beef heart in moderation, about 1–2 times per week, to avoid overloading on specific nutrients.
What does beef heart taste like?
Beef heart has a rich, meaty flavor with a slightly denser texture than muscle cuts. Explore creative ways to enhance its flavor using lemon garlic butter
How do you store leftover beef heart?
Store cooked beef heart in an airtight container in the refrigerator for up to 3 days or freeze for longer storage. Check out tips for storing leftovers.
Are there ethical concerns with eating beef heart?
Some people prefer to consume organ meats as a way to reduce waste and honor the whole animal.
Where can I buy high-quality beef heart?
High-quality beef heart is available at local butcher shops, farmers’ markets, or online specialty meat stores.
How Often Should You Eat Beef Heart
Beef heart is a nutritious, affordable, and versatile addition to your diet. It offers high levels of protein, vitamins, and minerals while promoting cardiovascular health, energy levels, and muscle repair. Incorporating it into your meals 1–2 times per week allows you to enjoy its benefits while maintaining a balanced and varied diet.
Proper preparation and cooking techniques, like grilling, braising, or slow cooking, enhance its flavor and texture, making it a delicious option for many dishes. Remember to source high-quality beef heart and consume it in moderation to maximize health benefits without risks.
By understanding the nutritional value and incorporating beef heart thoughtfully, you can elevate your meals and improve your overall health.
